Notebook of Gerard Henderson Cowan - Part 9




-PERMANENT MAGNETS-
Hand drawn diagrams - see original document
-Magetism-
field travel from the north end
to the south and, any metallic
substance affected by magnetism
if placed within this field of force
will try and set itself in the
same direction as the lines of forceIns These lines of force always
take the easiest path and
in the case of a horseshoe
magnet where the poles are
close together there is a
strong manetic field passing
from pole to pole
Two Laws of Magnetism
1st Like poles repel each other
2nd Unlike poles attract each other
Magnetism unlike Electricity
cannot be insulated.
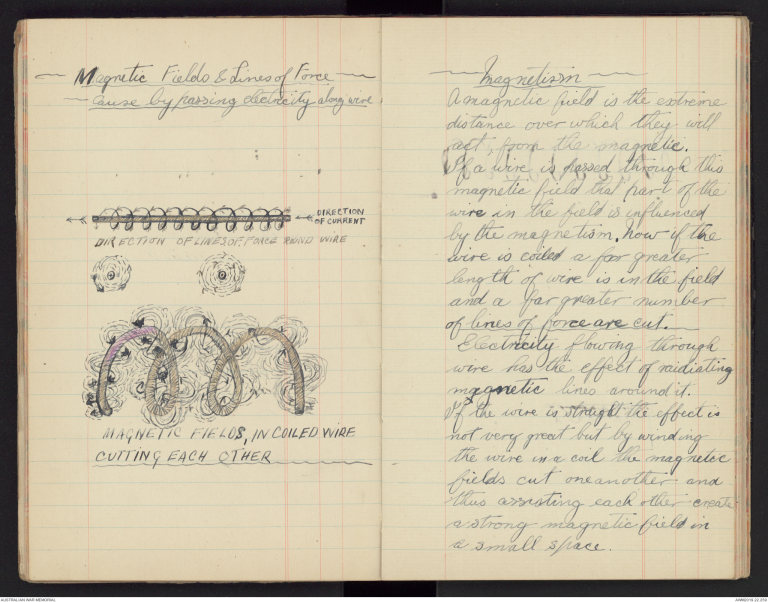
-Magnetic Fields & Lines of Force-
-Cause by passing electricity along wire
Hand drawn diagrams - see original document
-Magnetism-
A magnetic field is the extreme
distance over which they will
set from the magnetic.
If a wire is passed through this
magnetic field that part of the
wire in the field is influenced
by the magnetism. Now if the
wire is coiled a far greater
length of wire is in the field
and a far greater number
of lines of force are cut.
Electricity flowing through
wire has the effect of raidiating
magnetic lines around it.
If the wire is straight the effect is
not very great but by winding
the wire in a coil the magnetic
fields cut one another and
thus assisting each other create
a strong magnetic field in
a small space.
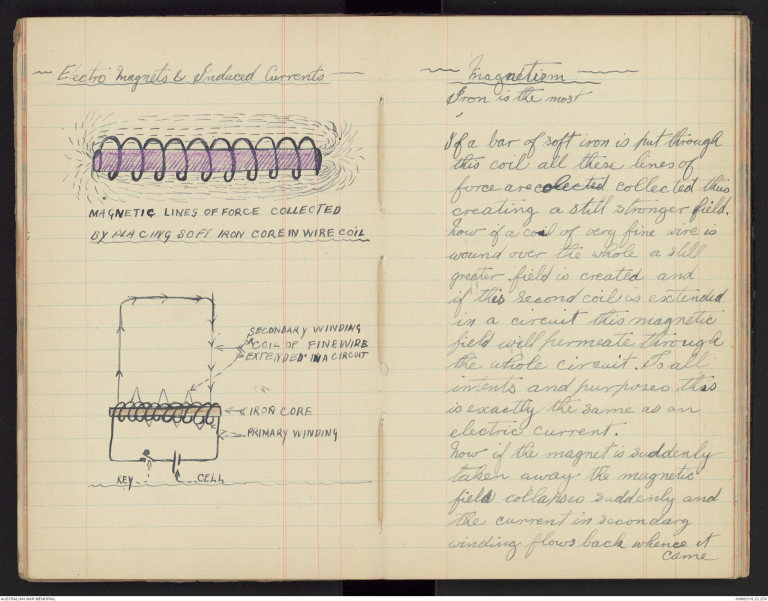
-Electro Magnets & Induced Currents-
Hand drawn diagrams - see original document
-Magnetism-
Iron is the most
If a bar of soft iron is put through
this coil all these lines of
force are colected collected thus
creating a still stronger field.
Now if a coil of very fine wire is
wound over the whole a still
greater field is created and
if this second coil is extended
in a circuit this magnetic
field will permeate through
the whole circuit. To all
intents and purposes this
is exactly the same as an
electric current.
Now if the magnet is suddenly
taken away the magnetic
field collapses suddenly and
the current in secondary
winding flows back whence it
came
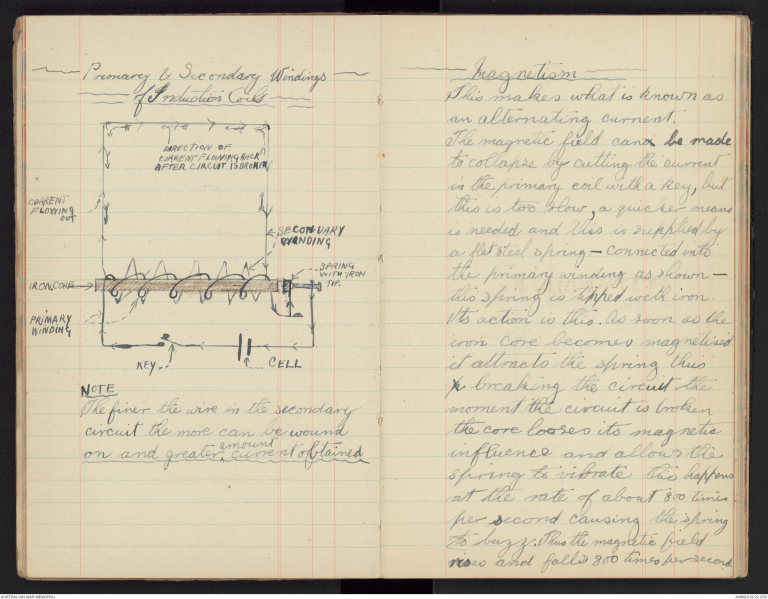
-Primary & Secondary Windings-
-of Induction Coils-
Hand drawn diagrams - see original document
NOTE
The finer the wire in the secondary
circuit the more can be wound
on and greater ^amount current obtained
-Magnetism-
This makes what is known as
an alternating current.
The magnetic field cand be made
to collapse by cutting the current
in the primary coil with a key, but
this is too slow, a quicker means
is needed and this is supplied by
a flat steel spring - connected into
the primary winding as shown -
this spring is tipped with iron
Its action is this. As soon as the
iron core becomes magnetised
it attracts the spring thusp breaking the circuit the
moment the circuit is broken
the core looses its magnetic
influence and allows this
spring to vibrate this happens
at the rate of about 800 times
per second causing the spring
to buzz. Thus the magnetic field
rises and falls 800 times per second
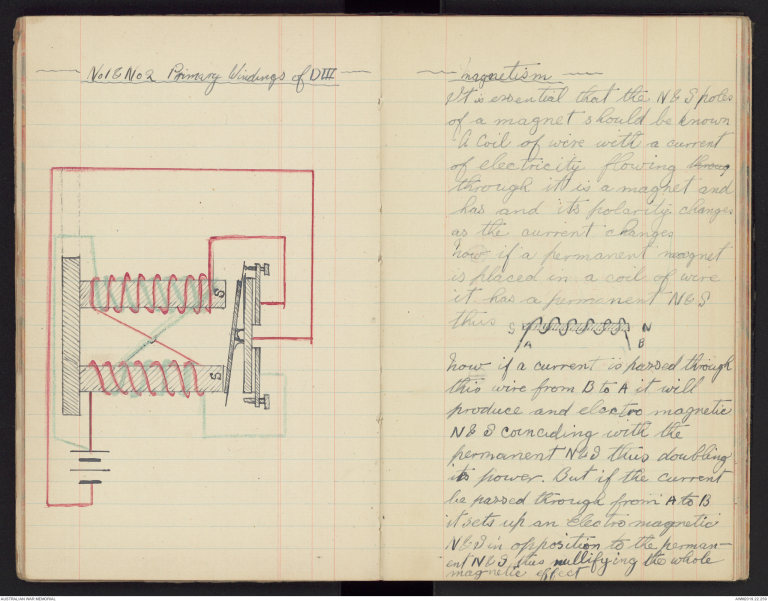
-No 1 & No 2 Primary Windings of D III-
Hand drawn diagram - see original document
-magnetism-
It is essential that the N & S poles
of a magnet should be known
A coil of wire with a current
of electricity flowing throug
through it is a magnet and
has and its polarity changes
as the current changes
Now if a permanent magnet
is placed in a coil of wire
it has a permanent N & S
thus
Hand drawn diagram - see original document
Now if a current is passed through
this wire from B to A it will
produce and electro magnetic
N & S coinciding with the
permanent N & S thus doubling
its power. But if the current
be passed through from A to B
it sets up an Electro magnetic
N & S in opposition to the permanent
N & S thus nullifying the whole
magnetic effect
Hand drawn diagram - see original document
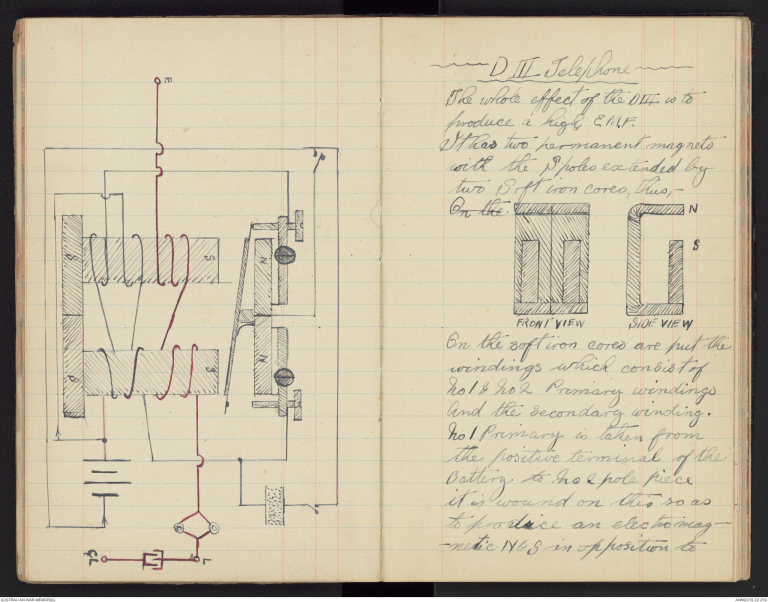
-D III Telephone-
The whole effect of the D III is to
produce a high E.M.F.
It has two permanent magnets
with the S poles extended by
two Soft iron cores, thus, -On the
Hand drawn diagram - see original document
On the soft iron cores are put the
windings which consist of
No 1 & No 2 Primary windings
and the secondary winding.
No 1 Primary is taken from
the positive terminal of the
Battery to No 2 pole piece
it is wound on this so as
to produce an electro magnetic
N & S in opposition to
-D III Telephone-
to the permanent N & S of that pole
thus making it loose its magnetic
effect. The winding is then
taken to No 1 pole and wound on
this, so as to strengthen the
magnetic field and is then
lead up to No 1 contact screw
the circuit is then completed
by a wire leading from a terminal,
connected with the armature,
back to the negative of the
battery.
The effect of passing a current
through this winding is to
attract the armature
and draw it away from No 1
contact screw thus breaking
the current in No 1 Primary winding
and making it in No 2.
Now No 2 winding is wound
just the reverse to No 1
-D III Telephone-
It leads on from the positive
terminal of the battery and
is wound on No 1 pole piece so as
to nullify the magnetic effect
and on No 2 so as to strengthen
it thus attracting the armature
down, breaking No 2 circuit
and making No 1 again. This
takes place at the rate of
800 times per second.
The Secondary winding,
which is composed of so fine
a wire as is possible so as
to be able to wind as much
as possible into the magnetic
field, may be wound on
either way provided it is
wound differently on
each pole piece.
Now the effect of the rapid
rise and fall of the magnetic
-D III Telephone-
field caused by the armature
making and breaking, is to
produce a high E.M.F. flowing
out in the secondary winding
every time the field rises and
and a higher E.M.F. still (flowing
in the opposite direction) every
time it falls.
One end of secondary winding is
connected to earth the other
to line thus when ^two instruments
are connected up they have a
complete circuit out through
the line and back through
the earth.
There is no means of detecting
this current in the secondary
except by a detector and
the most practicable detector
is the receiver.
Hand Drawn Diagram - see original document
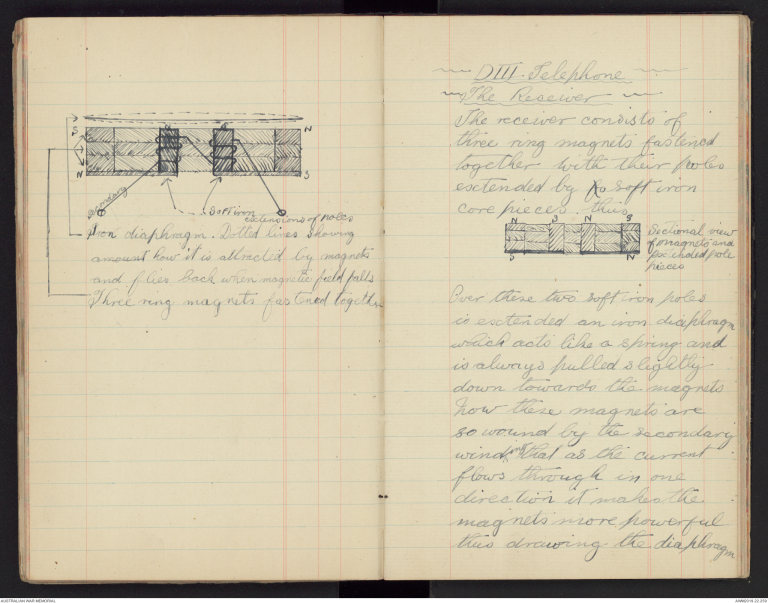
-D III Telephone-
-The Receiver-
The receiver consists of
three ring magnets fastened
together with their poles
extended by fo Soft iron
core pieces. thus
Hand drawn diagram - see original document
Over these two soft iron poles
is extended an iron diaphragm
which acts like a spring and
is always pulled slightly
down towards the magnets
Now these magnets are
so wound by the secondary
winding that as the current
flows through in one
direction it makes the
magnets more powerful
thus drawing the diaphragm
 Tracy Wright
Tracy WrightThis transcription item is now locked to you for editing. To release the lock either Save your changes or Cancel.
This lock will be automatically released after 60 minutes of inactivity.